Rack cabinet design for schools, smart classroom integration, campus network planning and server room organization explained in one practical guide.
Schools today rely on rack cabinets to organize network switches, wireless controllers and media servers. They also hold other gear that keeps learning spaces connected. A well-planned rack cabinet protects equipment from dust and accidental knocks. It also gives IT staff quick access for updates and repairs. In every smart classroom, that reliability keeps the campus network running smoothly and the server room stable.
Whether you manage one smart classroom or support a sprawling campus network, getting the cabinet design right matters. It means fewer service calls and smoother daily operation. This guide walks through practical choices that help server room setups and hallway closets stay tidy and cool. It also keeps them ready for the next wave of classroom technology.
Overview of Rack Cabinet Design in Schools
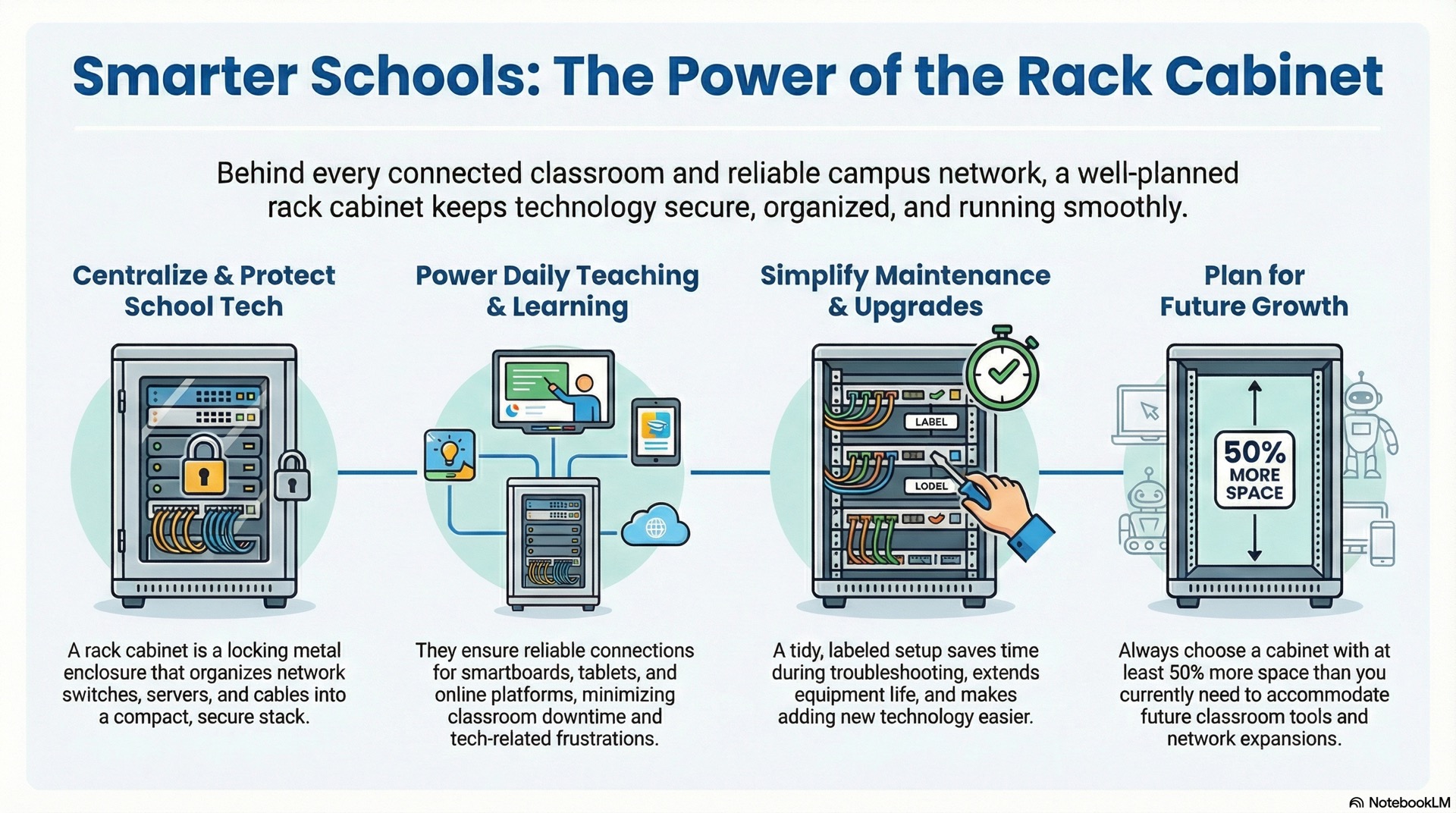
What Rack Cabinets Do in Learning Spaces
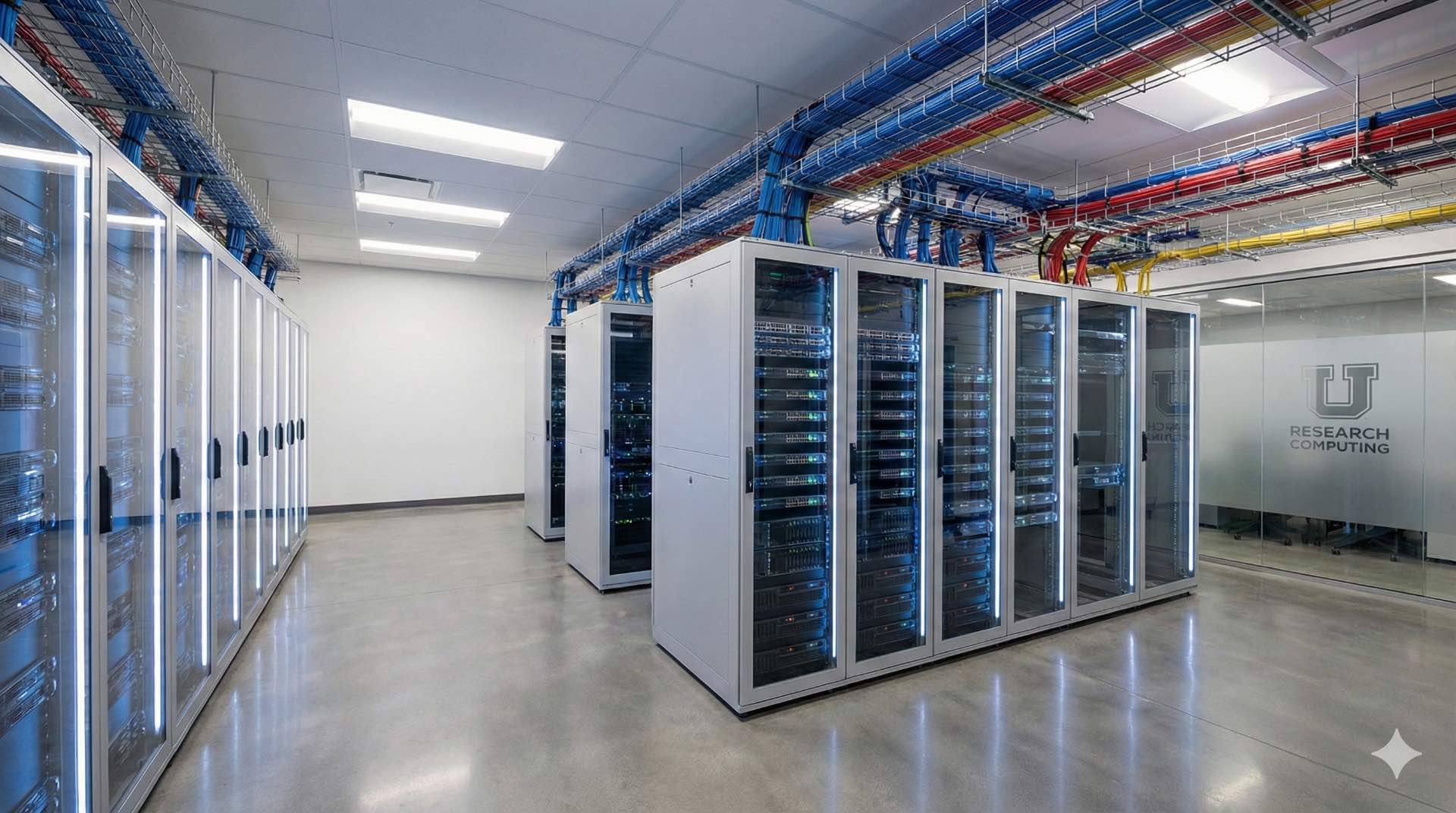
A rack cabinet is a metal enclosure with standard mounting rails. These rails hold switches, patch panels, power strips and other devices in a compact vertical stack. Schools use them to centralize network gear close to classrooms or in a dedicated server room. This keeps cables organized and equipment out of harm’s way.
The cabinet locks shut so only trained staff can reach live ports and power supplies. Ventilation slots or fans built into the cabinet keep air moving around warm switches and wireless controllers. By grouping everything in one secure box, you cut down on tangled wires. You also reduce the chance that a student or cleaner will unplug something critical.
How They Support Day-to-Day Teaching
Teachers expect displays, tablets and laptops to connect the moment class starts. Behind the scenes, a rack cabinet holds the network switches that route every device to the internet and the campus network. When a projector streams video or a student submits homework through the learning platform, data flows through patch cables inside the cabinet. Neatly dressed cables make that data path easy to trace.
If one cable comes loose or one switch needs a firmware update, IT staff open the cabinet door. They trace the labeled cables and fix the problem in minutes. Clean organization inside the rack cabinet means less downtime and fewer frustrated teachers waiting for a technician.
Benefits of a Neat and Protected Setup
A tidy rack cabinet saves time during troubleshooting. Every cable follows a clear path and every port carries a label. Dust filters on the cabinet doors keep dirt off sensitive electronics. This extends the life of your investment. Locked panels stop curious hands from unplugging or pressing reset buttons.
When you add a new smart classroom or expand wireless coverage, spare rack space and pre-run conduit let you mount extra switches. You can do this without tearing open walls. Schools that plan their cabinets well spend less on emergency repairs and enjoy smoother upgrades as teaching methods evolve.
Where Technology Cabinets Are Located on Campus
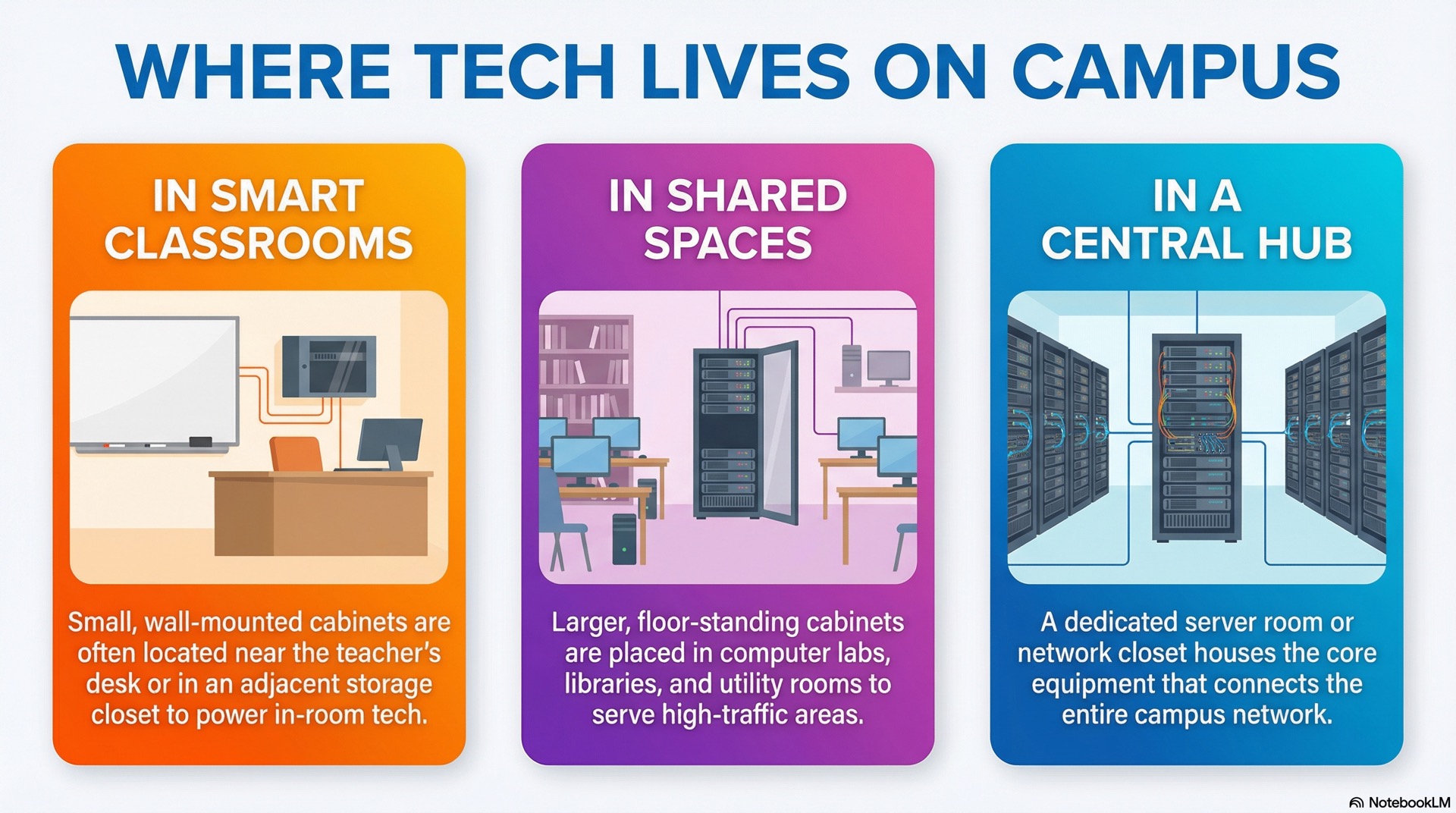
Smart Classrooms and Media-Rich Rooms
A smart classroom typically includes an interactive display, document camera and wireless access point. It may also have a media server or streaming device. Many schools mount a small wall-hung cabinet near the teacher’s desk or in an adjacent storage closet. This placement shortens cable runs from the display and microphone system to the network switch. Shorter cables mean less signal loss and easier cable management.
If you choose a ventilated smart classroom rack cabinet with quiet fans, noise stays low. Students barely notice the equipment humming a meter away. Locking the cabinet keeps cleaning staff and students from accidentally bumping a power strip. It also prevents them from yanking an HDMI cable.
Computer Labs, Libraries and Shared Areas
Computer labs and libraries often serve dozens of devices at once. A floor-standing cabinet near the lab entrance or behind the librarian’s counter centralizes the network switches. Those switches feed each workstation. You might also house a wireless controller in the same cabinet. This lets you manage access points scattered across the library.
Shared areas like cafeterias or auditoriums sometimes need their own cabinets. These support Wi-Fi and digital signage. Placing the rack cabinet in a locked utility room or closet protects it from spills. It also keeps foot traffic from bumping the enclosure during busy lunch periods.
Central Rooms That Serve the Whole School
Larger campuses maintain a server room or network closet that houses core switches, routers, firewalls and sometimes file servers. This central rack cabinet connects to smaller cabinets in classrooms and labs. It uses fiber or copper backbone cables for these connections. The campus network radiates out from here, so power and cooling become more critical.
A dedicated air conditioner or split system keeps the server room below 25 °C even when switches run at full load. Battery backup units inside the cabinet typically offer around fifteen to thirty minutes of runtime during a power cut. This gives the campus network time to shut down gracefully or lets you switch to a generator.
Keeping the server room locked and monitored with a simple door sensor adds a layer of security. This prevents unauthorized changes.
Planning the Right Rack Cabinet for Your Facility

Listing Today’s Devices and Future Additions
Start by counting every piece of active gear you plan to install. A typical smart classroom might need one network switch, one wireless controller or access point, one power strip and one patch panel. Write down the rack-unit height for each device. Most switches occupy one or two rack units. Patch panels and power strips each take one unit.
Add everything together and multiply by 1.5 to leave room for growth. If your total comes to twelve rack units, consider a cabinet that offers eighteen or twenty-four units of usable space. This buffer lets you add another switch when the school opens a new wing. It also helps when you upgrade to higher-capacity access points.
Choosing Rack Cabinet Size and Layout
Rack cabinets come in standard widths of 19 inches between the mounting rails. Height varies from short six-unit wall boxes to tall 42-unit floor cabinets. Depth ranges from shallow 450 mm enclosures suitable for patch panels and switches to deep 800 mm cabinets. The deeper cabinets accommodate servers with long cable-management arms. Schools with limited floor space often pick wall-mounted cabinets for individual classrooms. They reserve floor-standing models for the server room and other core spaces.
Check doorways and corridors before ordering a large cabinet. A 42-unit cabinet may be too tall or heavy to maneuver through a narrow hallway. You may need to remove doors first. Measure twice and confirm that installers can roll the cabinet into place on the delivery day.
Making Daily Access and Maintenance Easy
IT staff need to reach switches and patch panels without moving heavy furniture. They should not have to unscrew dozens of screws either. Choose a rack cabinet with a hinged front door that swings wide. Look for removable side panels held by quick-release latches. Transparent acrylic or perforated metal doors let you see link lights and labels without opening the cabinet.
If you mount the cabinet high on a wall, choose a sensible height. An average adult should be able to reach the top devices while standing on a small step stool. Avoid placing cabinets behind bookcases or filing cabinets that block access, especially in a small server room with limited space. Easy access means faster fixes and less frustration during the school day.
Keeping Rack Cabinets Cool, Powered and Tidy
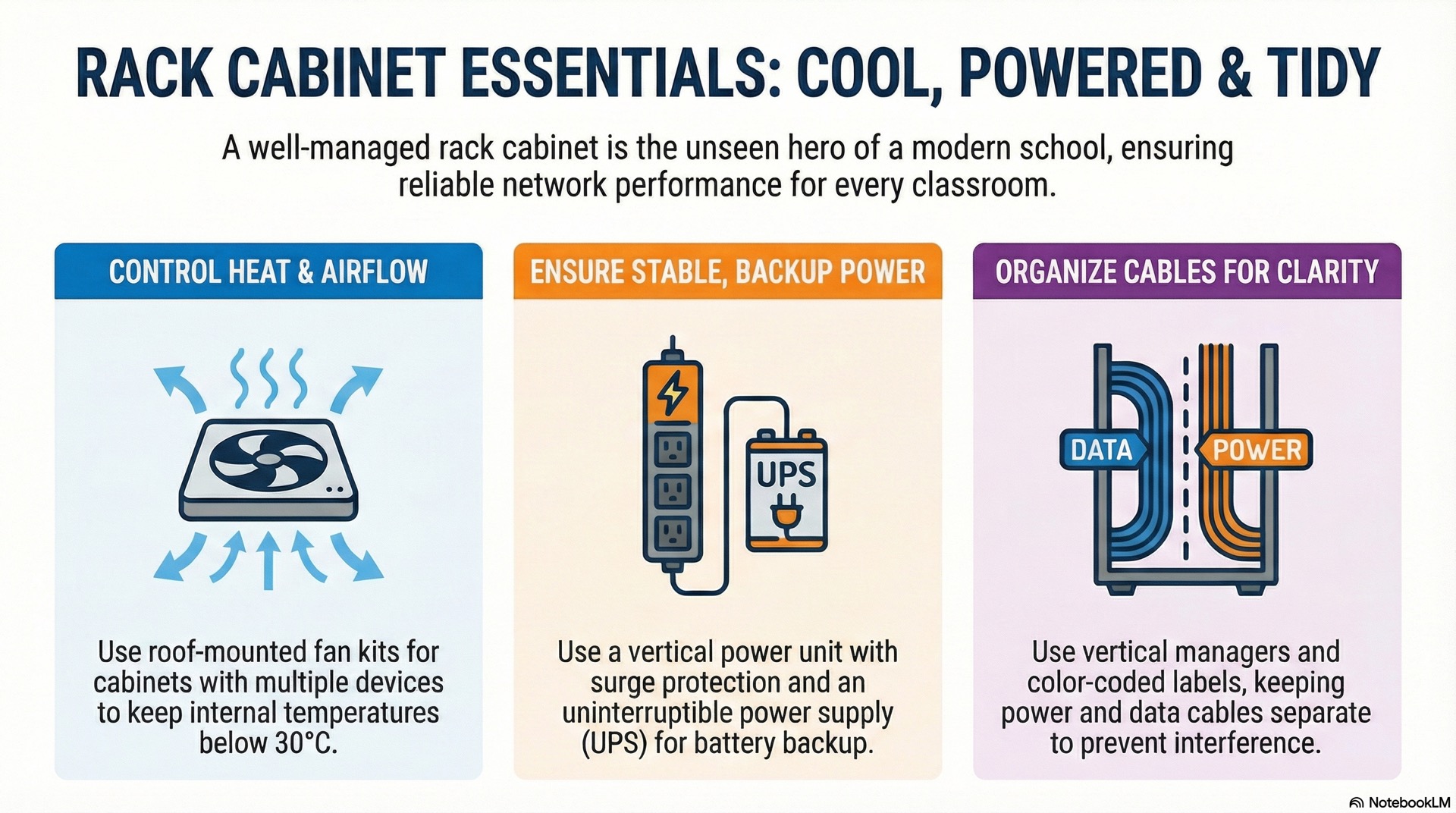
Simple Ways to Control Heat and Airflow
Network switches and wireless controllers generate heat as they process traffic. A rack cabinet traps warm air unless you provide ventilation. Passive cooling works for small setups with one or two low-power switches. This is typical in a smart classroom rack cabinet with minimal equipment. Perforated doors and side panels let air flow through the cabinet. Natural convection does the rest.
When you install multiple switches or a small server, add a roof-mounted fan kit. It pulls warm air out of the top of the rack cabinet and draws cooler room air in through the front vents. Aim for a temperature inside the cabinet that stays below 30 °C during peak usage. If the server room temperature climbs above that, consider a portable air conditioner or upgrade the room’s HVAC system.
Power, Backup and Basic Protection
Every device in the rack cabinet needs stable power. Mount a vertical power distribution unit along the rear rail so outlets sit close to each switch and controller. Choose a unit with surge protection. This guards against voltage spikes from lightning or grid faults. For critical gear in the campus network core, add an uninterruptible power supply that provides battery backup during outages. A small UPS rated for 500 to 1000 volt-amperes can often support one or two switches for around twenty minutes of buffer. This gives enough time to save configurations for a busy smart classroom or wait for a generator to start.
Label each power cable with the device it feeds. If you need to power down one switch for maintenance, you can unplug exactly the right cord. No guessing required.
Cable Paths and Labels Inside the Rack Cabinet
Tangled cables make troubleshooting a nightmare. Run network cables along the sides of the rack cabinet using vertical cable-management brackets. These brackets come with D-rings or plastic fingers that guide cables neatly. Secure bundles with reusable hook-and-loop straps instead of zip ties. Zip ties can pinch wires and create sharp edges. Keep power cables separate from data cables to avoid electromagnetic interference.
Use color-coded patch cables or printed labels on every plug. This way you know which port connects to which classroom or access point. A simple labeling scheme like “Room 101 – Port 1” beats cryptic codes that only one person understands. When you add or remove a cable, update the labels the same day. Clear labels save time and prevent accidental unplugs during routine work.
Safety and Security Around Rack Cabinets
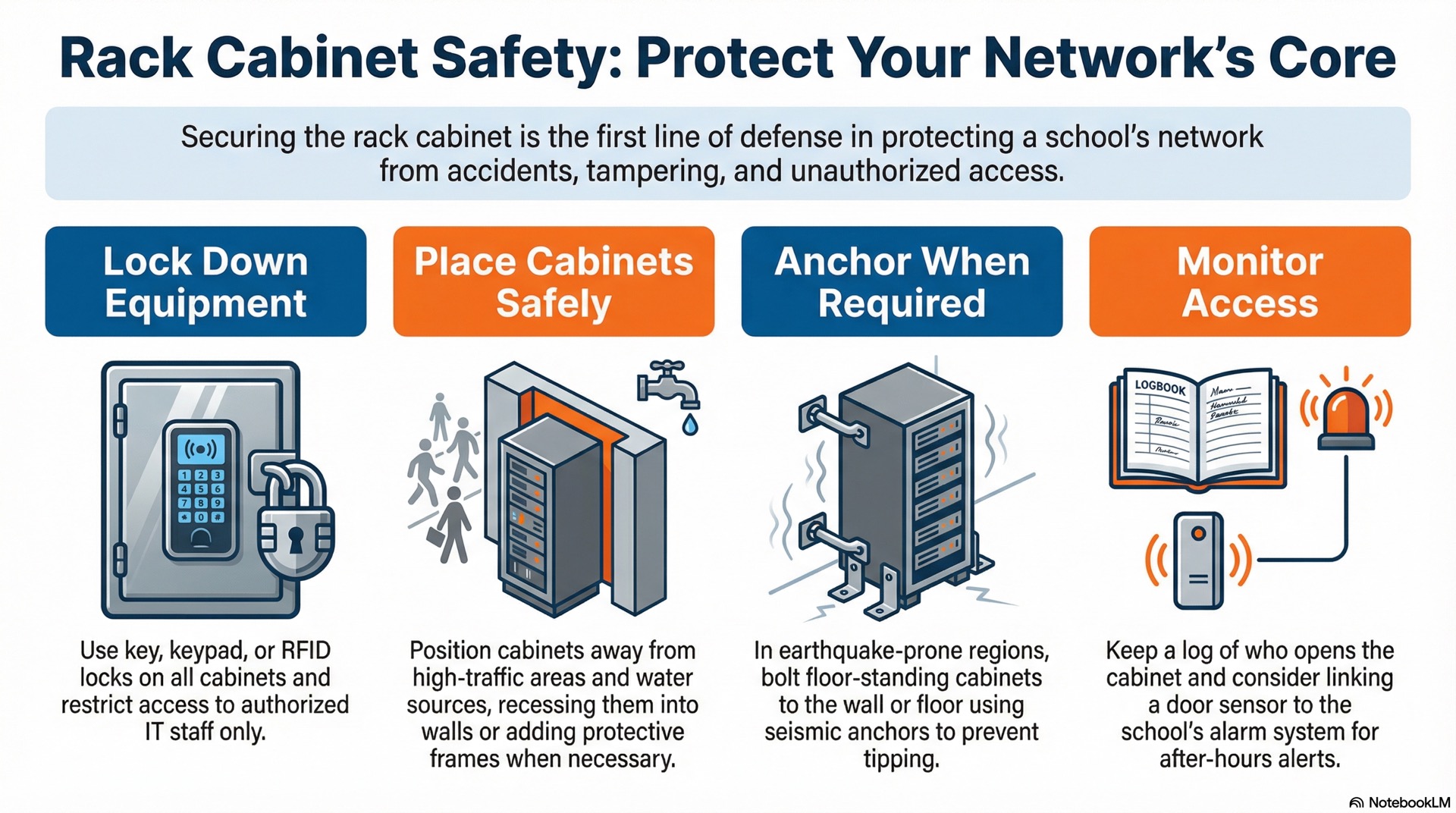
Controlling Who Can Reach the Equipment
Rack cabinets should lock to keep unauthorized people from tampering with switches or unplugging cables. Standard key locks work for most schools. Consider upgrading to keypad locks or RFID badges in high-security areas. Only issue keys or codes to IT staff and a few trusted administrators. Keep a log of who opens the cabinet and when. This is especially important in the server room where one wrong click can disrupt the entire campus network.
If your cabinet sits in a shared corridor, mount a motion sensor or door contact inside the cabinet. Link it to the school’s alarm system. This extra step alerts you if someone forces the lock after hours.
Placing Rack Cabinets Safely in Busy School Areas
Hallways and common areas see heavy foot traffic. If you must place a rack cabinet in a corridor, recess it into the wall. If that is not possible, protect it with a sturdy frame to prevent collisions. Make sure fire codes allow cabinets in exit routes. Some jurisdictions require minimum clearance around the cabinet. This lets students pass safely during an evacuation. Avoid putting cabinets near water fountains, sinks or janitor closets. Spills can seep through vents in these locations.
In earthquake-prone regions, bolt floor-standing cabinets to wall studs or concrete floors using seismic anchors. A toppled cabinet damages expensive gear and creates a safety hazard.
Reducing Noise and Distraction Near Classrooms
Fan noise from a rack cabinet can disrupt quiet study or testing sessions. Choose fans with low decibel ratings or install sound-dampening foam on the inside of cabinet doors. Some manufacturers offer silent or semi-passive cooling kits designed for office environments. If noise remains a problem, relocate the cabinet to a nearby storage room or hallway closet. Run slightly longer cables to the smart classroom rack cabinet.
Balance acoustics with cooling. A cabinet running too hot because you disabled the fan will fail sooner. This is worse than one humming softly in a closet ten meters away.
Future-Proofing Technology Spaces on Campus

Leaving Room for New Classroom Tools
Education technology changes fast. Today’s smart classroom runs on gigabit Ethernet. Tomorrow’s virtual-reality labs may need ten-gigabit uplinks or fiber connections. When you design your rack cabinet, reserve at least 30 percent of the space for future devices. Install extra conduit between the cabinet and ceiling or raised floor. This lets you pull new cables without cutting drywall.
Choose modular patch panels that accept different connector types. If you start with copper RJ45 jacks, you can swap in fiber modules later. You can do this without replacing the entire panel. Flexible infrastructure costs a bit more now. It can save major expense during the next campus upgrade.
Using Similar Layouts Across Different Buildings
A standardized rack cabinet layout makes it easier for IT staff to work across multiple buildings. If every smart classroom cabinet follows the same arrangement—switch on top, patch panel in the middle, power strip at the bottom—technicians always know where to look. They can walk into any room and start work immediately. Standardization also simplifies inventory. You stock one model of cabinet, one model of switch and one type of cable. Bulk purchasing lowers costs and reduces the chance of ordering incompatible parts.
Document your standard layout in a simple one-page diagram. Share it with contractors who install new cabinets. Consistency speeds up installations and cuts training time for new hires.
Keeping Simple Records for IT and Maintenance
A basic spreadsheet listing each rack cabinet on campus, its location and installed devices helps IT staff plan upgrades. Adding port assignments makes it easier to respond to outages. Take a photo of the inside of each cabinet after installation and store it in a shared folder. Update the photo whenever you add or remove equipment. This visual record makes it easy to verify configurations remotely or share context with a vendor during a support call.
Track warranty expiration dates for switches and UPS batteries so you can replace aging parts before they fail. Simple records prevent surprises and keep the campus network running smoothly year after year.
Schools that invest time in thoughtful rack cabinet design enjoy reliable campus network performance and fewer headaches when technology evolves. By choosing the right size cabinet and organizing cables clearly, you create a solid foundation. Planning for growth keeps today’s smart classroom tools ready for tomorrow’s innovations.
You might oversee one rack cabinet in a single smart classroom or manage IT for an entire campus network. In both cases, these practical steps help you build a tidy, secure and maintainable infrastructure. Teachers can focus on teaching and students can focus on learning, with server room stability backing every lesson.





